Ref. No. [UMCES] CBL 2015-012
ACT VS15-05
Great Lakes Field Test Site
A month-long moored field test was conducted in Lake Michigan from June 21 to July
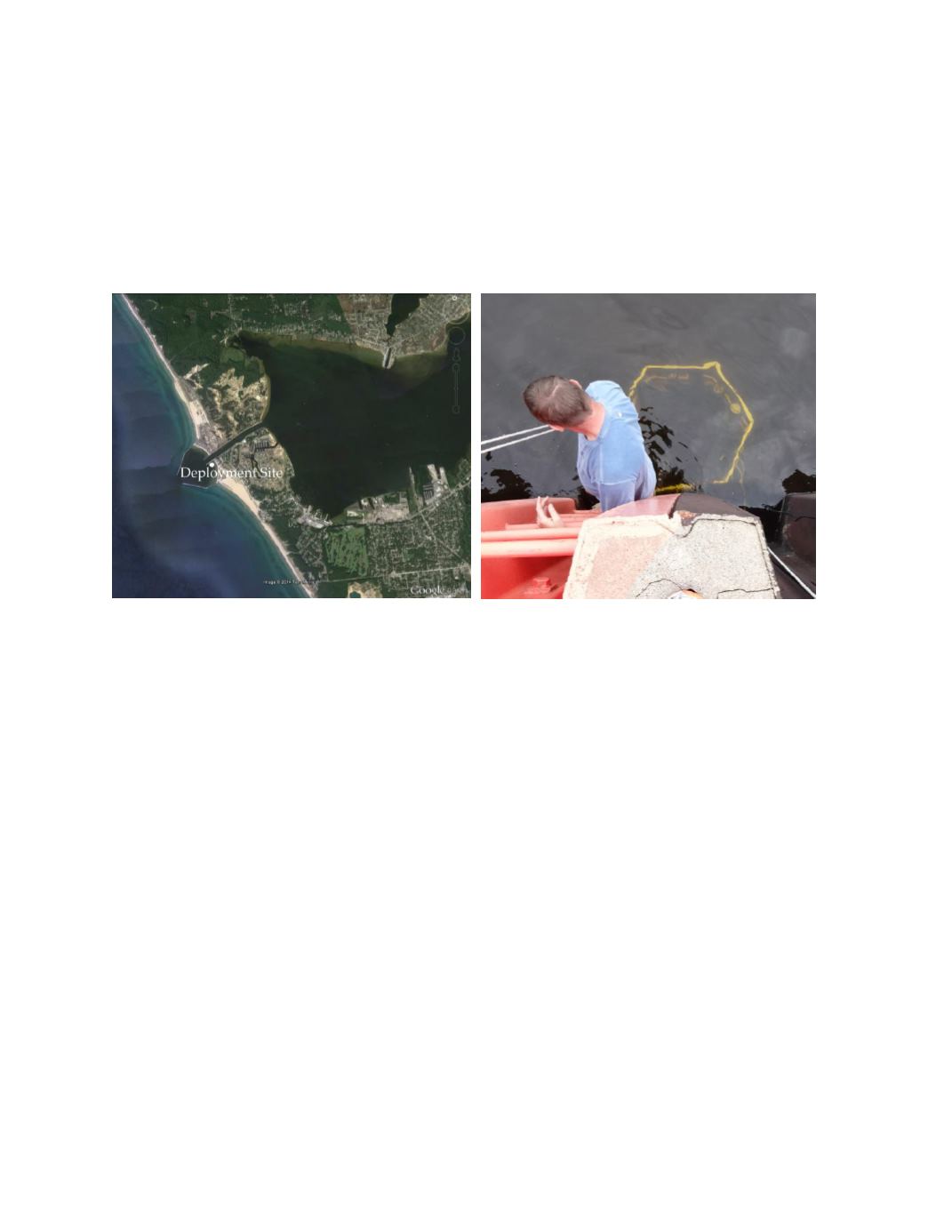
19, 2014. The Great Lakes deployment site was located at 43.23°N, 86.34°W on a fixed pier at
the Lake Michigan Field Station of the NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory,
in Muskegon, Michigan. The site is located at the outfall of Lake Muskegon into Lake Michigan
with a depth of approximately 3 meters. The temperature range during deployment was 11.6°C
through 24.9°C and salinity averaged 0.031.
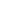
Photo 8.
Aerial view of Lake Michigan and Muskegon Lake (left) and rack deployment at GL Site
Time series results of ambient conditions for water depth, temperature, and salinity are
given in figure 12. Temperature ranged from 11.6 to 24.9 and salinity from 0.024 to .035 over
the duration of the field test. While there are no tidal cycles at this site there was significant
exchange between the open lake and the protected basin within the break wall as evidenced by
changes in salinity and water depth. The bottom panel displays the maximum difference recorded
between all reference thermistors (RBR Solo and SBE26) mounted at the same depth and
different locations across the mooring rack. The average temperature difference observed across
the space of the mooring rack was 0.08 ±0.18
o
C, with a maximum of 2.53
o
C. As noted above, it
is not possible to quantify the exact difference between the averaged reference temperature and
that measured by the test instrument, but differences resulting from this variation and variation in
the chemistry of the water across will be because the sampling bottle integrates across the
mooring space.
The SeaFET operated throughout the entire deployment and generated 2673 observations
based on its 15 minute sampling interval. It should be noted that only results from the internal
pH sensor are reported for this deployment site since the freshwater media does not allow the
external reference electrode to function properly. The internal pH sensor reported ambient pH
over a range from 7.770 to 8.594, compared to 8.013 to 8.526 captured by the reference pH
measurements (Fig. 13). The bottom panel presents the time series of the difference between the
SeaFET and reference pH for each matched pair (n=98 observations). The average and standard
deviation of the difference for the entire deployment was -0.183 ± 0.040 with a total range of -
0.347 to -0.090.