Ref. No. [UMCES] CBL 2016-013
ACT VS16-04
45
Great Lakes Profiling
Great Lakes profiling tests were performed aboard the R/V Laurentian at two separate
locations in order to experience both normoxic and hypoxic hypolimnion (Photo 7). The normoxic
site was located in Lake Michigan (43.184
°
N, 86.456
°
W) within a 64m deep water column, while
the hypoxic site was in Muskegon Lake at 43.22
°
N, 86.30
°
W with a 24m deep water column.
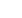
Photo 7.
Aerial view of Lake Michigan and Muskegon Lake (left) and profile rig used for GL profiling
Two profiling trials were conducted at each location. The first trial involved equilibrating
test instruments at the surface (3m) for ten minutes and then collecting three Niskin bottle samples
at one minute intervals. Following the third sample, the rosette was quickly profiled into the
hypolimnion where samples were collected immediately upon arrival and then each minute for the
next 6 minutes (figure 11 and 13). The second trial was performed in the reverse direction where
instruments were equilibrated at depth, three samples collected, and then profiled into the surface
and sampled over the next 7 minutes. Note for Muskegon Lake cast 1 was discarded due to bottle
misfires, so a third cast was performed to repeat the original trial 1 pattern (Fig. 11). It should be
emphasized these tests were not intended to demonstrate profiling capability but rather ability and
time response to equilibrate to large changes in temperature and DO over minute time scales.
Temperature and DO concentration profiles for Muskegon Lake and Lake Michigan are
given in figures 12 and 14, respectively. In Muskegon Lake, the temperature ranged from 21.0
o
C
at the surface to 13.5
o
C in the hypolimnion, with corresponding DO concentrations of 7.8 and 2.8
mg/L, respectively. In Lake Michigan, the temperature ranged from 21.0
o
C at the surface to 4.1
o
C in the hypolimnion, with corresponding DO concentrations of 8.6 and 12.6 mg/L, respectively.
Results for the HOBO U26 for the two Muskegon Lake trials are shown in figure 15. For
cast 2, the HOBO was well matched during equilibration in the hypolimnion but then showed a
strong positive bias when rapidly transitioned to the warmer, normoxic surface. The sensor did not
fully equilibrate after 7 minutes and remained around 0.7 mg/L higher than reference values. For
cast 3, the HOBO exhibited an initial 0.5 mg/L offset during equilibration at the surface and then
showed an initial negative offset of -0.9 mg/L when rapidly transitioned to the colder, low DO